Mariotte Bottle
Mariotte Bottle Specification
- Classification
- Soil Testing Equipment / Fluid Control Equipment
- Application
- Preclinical safety studies
- Automation Grade
- Manual
- Color
- White
- Usage
- Soil permeability test, constant head test
- Product Type
- Mariotte Bottle
- Warranty
- 1 Year
- Temperature Range
- 10C to +120C Celsius (oC)
- Type
- Pharmacology & Physiology Instrument
Mariotte Bottle Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Unit
- Payment Terms
- Cash Advance (CA)
- Supply Ability
- 10 Units Per Month
- Delivery Time
- 4 Week
- Main Export Market(s)
- Australia, South America, Western Europe, Middle East, Central America, Asia, Eastern Europe, North America, Africa
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About Mariotte Bottle
FAQs of Mariotte Bottle:
Q1. What is a Mariotte Bottle?
A1. A Mariotte Bottle is a laboratory device used to supply a constant and steady flow of liquid, regardless of the decreasing liquid level inside the container.
Q2. How does a Mariotte Bottle work?
A2. It works on the principle of maintaining constant hydrostatic pressure. An air inlet tube regulates the pressure inside, ensuring a uniform liquid flow rate.
Q3. What are the main applications of a Mariotte Bottle?
A3. It is commonly used in soil permeability tests, infiltration studies, hydrology experiments, and other laboratory setups requiring a steady flow of liquid.
Q4. What materials are Mariotte Bottles made of?
A4. They are generally made from glass, acrylic, or plastic depending on laboratory requirements and chemical compatibility.
Q5. Why is a Mariotte Bottle important in soil testing?
A5. In soil permeability and infiltration experiments, it ensures a constant water head for accurate and reliable test results.
Reliable Solution for Soil Permeability Tests
Optimize soil analysis in laboratory and field settings with the Mariotte Bottle. Used extensively for constant head tests, it ensures consistent water flow rates, vital for accurate soil permeability measurements. Its adaptable temperature range supports various experimental conditions, making it indispensable for soil scientists and researchers.
Precision Fluid Control for Preclinical Studies
Engineered for pharmacology and physiology labs, the Mariotte Bottle provides controlled liquid dispensing needed in preclinical safety studies. Its manual operation allows for hands-on regulation, while the durable design suits frequent use. The instruments white finish aligns with clinical environments, supporting seamless integration into study workflows.
FAQs of Mariotte Bottle:
Q: How does the Mariotte Bottle maintain a constant flow rate during soil permeability tests?
A: The Mariotte Bottle remains filled to a specific level, ensuring a constant hydrostatic pressure that delivers a steady water flow. This is essential for accurate constant head tests used in soil permeability studies.Q: What is the process for using the Mariotte Bottle in preclinical safety studies?
A: To use the Mariotte Bottle, fill it with the required liquid and set it up to deliver a controlled, constant flow to your experimental setup. It is especially useful for procedures needing precise fluid control, such as preclinical pharmacology and physiology experiments.Q: When should I use the Mariotte Bottle in soil testing or laboratory experiments?
A: You should employ the Mariotte Bottle whenever consistent fluid flow is needed, particularly in soil permeability and constant head tests. Its wide temperature range makes it suitable for both low- and high-temperature applications.Q: Where can I purchase the Mariotte Bottle in India?
A: The Mariotte Bottle is available from leading distributors, exporters, manufacturers, and suppliers located across India. You can contact these providers for national and international delivery, product details, and warranty information.Q: What benefits does a manual Mariotte Bottle offer over automated options?
A: A manual Mariotte Bottle allows for direct user control, offering flexibility during setup and experimentation. Its less susceptible to technical failures, making it reliable for field use and labs with limited automation capabilities.Q: How does the wide temperature range enhance the Mariotte Bottles applications?
A: With a temperature range from 10C to +120C, the Mariotte Bottle can be used in diverse environments, from refrigerated studies to heated experimental procedures, ensuring consistent performance.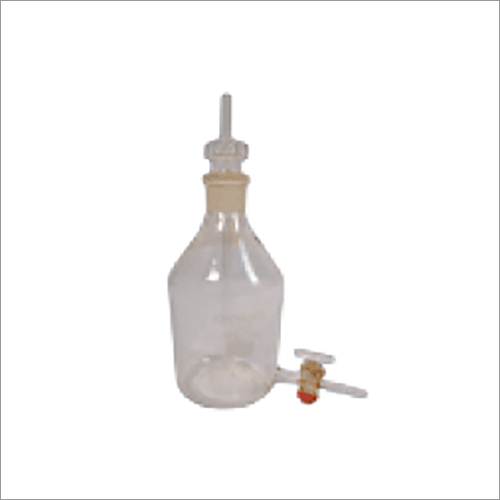

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
 Maharashtra, India
Maharashtra, India Mon-Sat 9.00 AM to 6.00 PM
Mon-Sat 9.00 AM to 6.00 PM

 Call Me Free
Call Me Free
